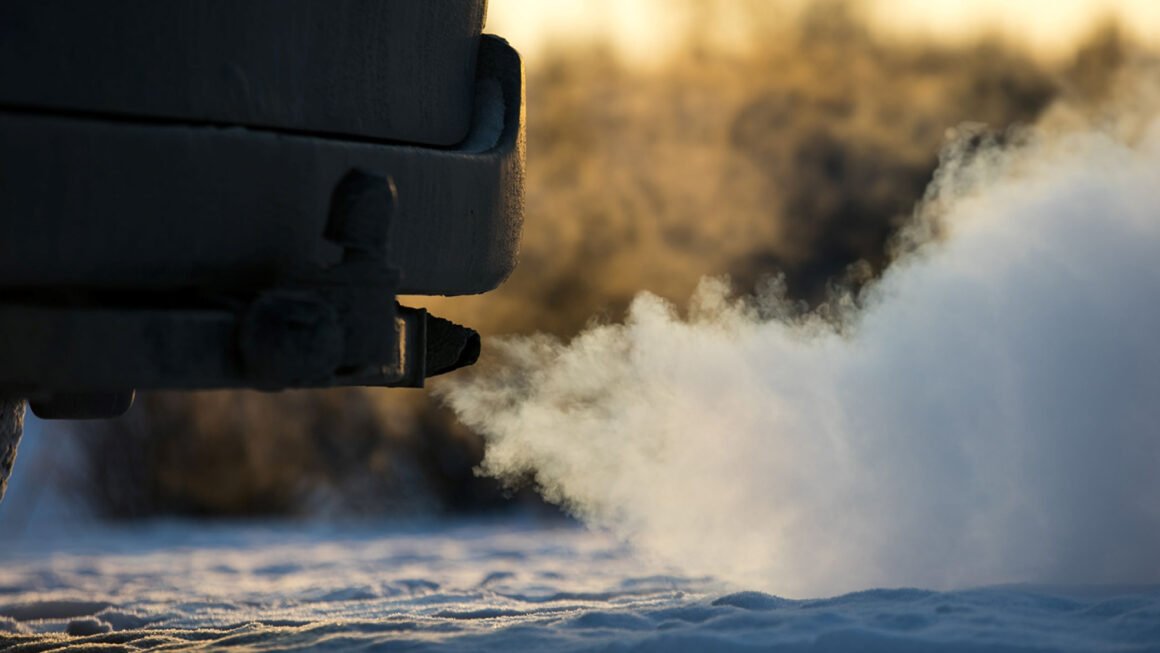
Carbon Footprint of Cars: A Comprehensive Exploration
In an era of increasing environmental consciousness, understanding the environmental impact of our choices, including the vehicles we drive, has become paramount. One crucial metric that sheds light on a car’s environmental contribution is its “carbon footprint.” In this article, we delve into the intricacies of a car’s carbon footprint, unraveling what it is, how it’s calculated, the accepted levels, and its relevance to drivers.
Defining Carbon Footprint:
A car’s carbon footprint represents the total amount of greenhouse gases, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), and other pollutants emitted throughout its lifecycle, from manufacturing and fuel production to operation and eventual disposal.
How it’s Calculated:
- Manufacturing Emissions:
- The production of a car involves energy-intensive processes, contributing to its carbon footprint. This includes the extraction and processing of raw materials, manufacturing, and transportation of components.
- Operational Emissions:
- The primary source of operational emissions is the combustion of fuel. The type of fuel used, fuel efficiency, and driving conditions all factor into the carbon footprint during the car’s lifetime.
- End-of-Life Emissions:
- Disposing of a car also generates emissions, primarily from the recycling or landfilling of materials. The carbon footprint includes these end-of-life considerations.
Accepted Levels and Why They Matter:
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) estimates that limiting global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels requires net-zero carbon emissions by 2050. This means drastically reducing our current footprint, including that of transportation.
Transportation, particularly cars, is a major culprit in greenhouse gas emissions. In the U.S. alone, cars and trucks account for nearly 60% of transportation emissions and 29% of total greenhouse gas emissions. Reducing car-related emissions is crucial for mitigating climate change and its devastating consequences, like rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and disruptions to ecosystems.
Relevance to Drivers:
- Economic Benefits:
- Cars with lower carbon footprints are often more fuel-efficient, resulting in cost savings for drivers. Reduced fuel consumption translates to fewer emissions and a smaller carbon footprint.
- Environmental Responsibility:
- Drivers can make informed choices by opting for vehicles with lower carbon footprints, contributing to the collective effort to minimize the environmental impact of transportation.
Effects of a Car’s Carbon Footprint:
- Climate Change Impact:
- A higher carbon footprint contributes to climate change, as greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere. Lowering a car’s carbon footprint helps mitigate its contribution to global warming.
- Air Quality:
- Vehicles with higher carbon footprints often emit more pollutants that contribute to poor air quality. Choosing low-emission vehicles positively impacts local air quality and public health.
- Resource Conservation:
- Lowering a car’s carbon footprint promotes resource conservation by encouraging sustainable manufacturing practices and reducing the demand for finite resources.
Conclusion:
By understanding and addressing our car’s carbon footprint, we can take a crucial step towards a cleaner, healthier planet. Remember, it’s not just about the car you drive, but how you drive and the choices you make. Every conscious effort, from choosing an eco-friendly vehicle to opting for car-free alternatives, contributes to a more sustainable future for all. So, be mindful of your car’s hidden footprint, and together, let’s pave the way for a low-carbon future.
Add a comment Cancel reply
Categories
- Car Gadgets (17)
- Car News (33)
- Car Reviews (43)
- Car Wars (7)
- Mechanicals (32)
- Uncategorized (2)
Recent Posts
About us

Popular Tags
Related posts


The New Car Smell: What you need to Know

The Drawbacks of Stretched Sedans: Cruising in Comfort or Compromising Convenience?